V. Theory and applications of integrating spheres
Integrating spheres are very versatile optical elements, which are designed to achieve homogenous distribution of optical radiation by means of multiple Lambertian reflections at the sphere's inner surface. The primary radiation source can be located either inside the sphere or in front of the source's entrance port. In the latter case, only the optical radiation entering the sphere is relevant for the sphere's internal radiation distribution. As long as we restrict ourselves to those regions which are shielded from direct irradiation by the primary source and are thus only illuminated by reflections at other of the inner surface, the theory of the ideal integrating sphere leads to two important conclusions:
- Irradiance of the sphere's inner surface is proportional to the total radiant power either emitted by a source inside the sphere or entering the sphere through its entrance port. Geometrical and directional distribution of the primary source's radiation do not influence irradiance levels as long as direct illumination of the respective location is prevented. This property becomes especially important when an integrating sphere is used as the input optical element of a detector for radiant power (see § III.1.b).
- Radiance reflected by a region of the sphere's inner surface shielded from direct illumination is constant in its directional distribution and independent from the specific location where the reflection occurs. Thus, the sphere's exit port can be used as an ideal Lambertian source as optical radiation leaving the sphere is characterised by homogenous radiance and exitance distributions. This property becomes especially important when a sphere is used as a standard calibration source.
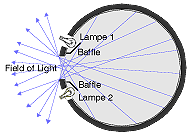
Fig. V.1. Integrating sphere used as a standard source for optical radiation. Multiple Lambertian reflections inside the sphere result in a homogenous radiance and exitance distributions at the sphere's exit port.
Download our Tutorials On Light Measurement. Size: 3 MB
Practical Solutions to Real Light Measurement Problems
Here's The Problem:
As an applied optics professor at university you would like to set-up an optical properties of materials experiment in your lab course to demonstrate single and double beam reflectance and transmittance measurement of various samples with different thicknesses at both +/- 8-degree and 0 degree geometries. Space and budget are limited so a compact device with maximum flexibility would be ideal.
Here's The Requirements:
- Integrating sphere base unit designed for reflectance transmittance measurements
- Multiple port layout for flexibility in experiment set-up
- Quick and easy means of mounting optional sphere components onto the ports
- Full complement of reflection and transmission based sphere components like adjustable sample holders, port reducers, detectors, light traps and light sources
- Small footprint for post-mounted or bench-top usage
- Capability for use as an integrating sphere source for calibration purposes
Here's The Solution:
Gigahertz-Optik's UPB-150-ART Universal R/T/ULS Integrating sphere with fifteen different reflection, transmission and self-absorption correction set-ups and full line of UPB-150-ART-ZXX accessory components.
Interested in discussing your integrating sphere application?
Give us a call!

